
When this involves large-scale networks involving many millions of customers this may effectively partition a part of the Internet involving those carriers, especially if they decide to disallow routing through alternate routes. Such disruptive de-peering has happened several times during the first decade of the 21st century.

Peering is founded on the principle of equality of traffic between the partners and as such disagreements may arise between partners in which usually one of the partners unilaterally disconnects the link in order to force the other into a payment scheme. Traffic from one network to the other is then primarily routed through that direct link.Ī Tier 1 network may have various such links to other Tier 1 networks. The NSFnet-supplied regional networks then sought to buy national-scale Internet connectivity from these now numerous, private, long-haul networks.Ī bilateral private peering agreement typically involves a direct physical link between two partners. New Tier 1 ISPs and their peering agreements supplanted the government-sponsored NSFNet, a program that was officially terminated on April 30, 1995. The network routing architecture then became decentralized and attained a need for exterior routing protocols, in particular the Border Gateway Protocol emerged. When the Internet was opened to the commercial markets, multiple for-profit Internet backbone and access providers emerged. Such was the weight of the NSFNET program and its funding ($200 million from 1986 to 1995)-and the quality of the protocols themselves-that by 1990 when the ARPANET itself was finally decommissioned, TCP/IP had supplanted or marginalized most other wide-area computer network protocols worldwide.
The Internet could be defined as the collection of all networks connected and able to interchange Internet Protocol datagrams with this backbone. NSFNET (1985) infrastructure programs to serve their nations' higher education communities, regardless of discipline, resulted in 1989 with the NSFNet backbone. The development of the British JANET (1984) and U.S. The original Internet backbone was the ARPANET when it provided the routing between most participating networks. Tier 3 network: A network that solely purchases transit/peering from other networks to participate in the Internet.
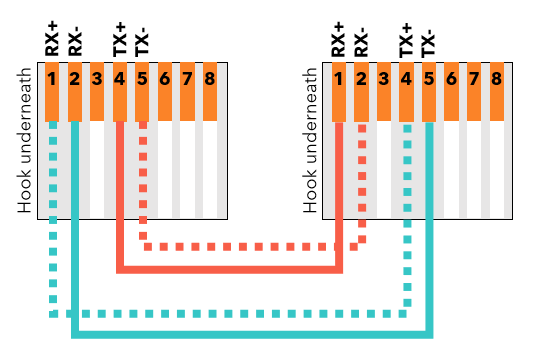
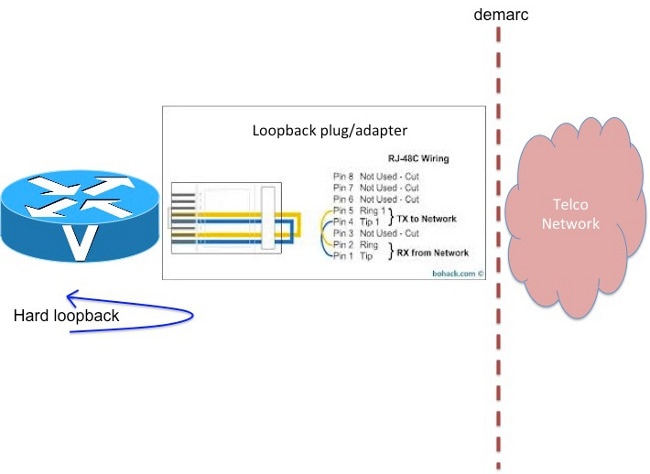
#Tier 1 loopback cable for free#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
